Photometric Redshifts of Galaxies
Presented by 钟其燊, 张子恒, 刘烨宇 & 刘乐融2025.12.25
Contents
- Review of Previous Research
- Reproduction of the Color Cut
- Crossmatching data from CLAUDS & DESI
- Training & Comparison
What is LBGs?
LBGs (Lyman break galaxies) are young and actively star-forming galaxies that make up most of the population of star-forming galaxies at $z > 1.5$.
They are rich in HI so they have a distinctive break at wavelengths shorter than the Lyman limit ($912\text{ \AA}$, rest-frame) and a decrement of flux shortward of the Lyman-$\alpha$ (Ly$\alpha$) spectral feature ($1216\text{ \AA}$, rest-frame).
What can we do with LBGs?
LBG appear to be promising tracers to carry out 3d clustering measurements in the redshift range $2 < z < 4$.
Compared with Ly$\alpha$ forest measurements from high redshift quasars (QSOs), LBGs have more samples in low redshifts.
How to select LBGs for spectral observation?
The distinct break at Lyman limit will redshift to visual band: \[\lambda_\text{obs} = \lambda_\text{em} (1 + z)\]
With redshifts $> 2$, the lyman limit will move to $u$-band, which can be observed by dropout method.
This is an AI-generated image to help understand the LBG spectra.
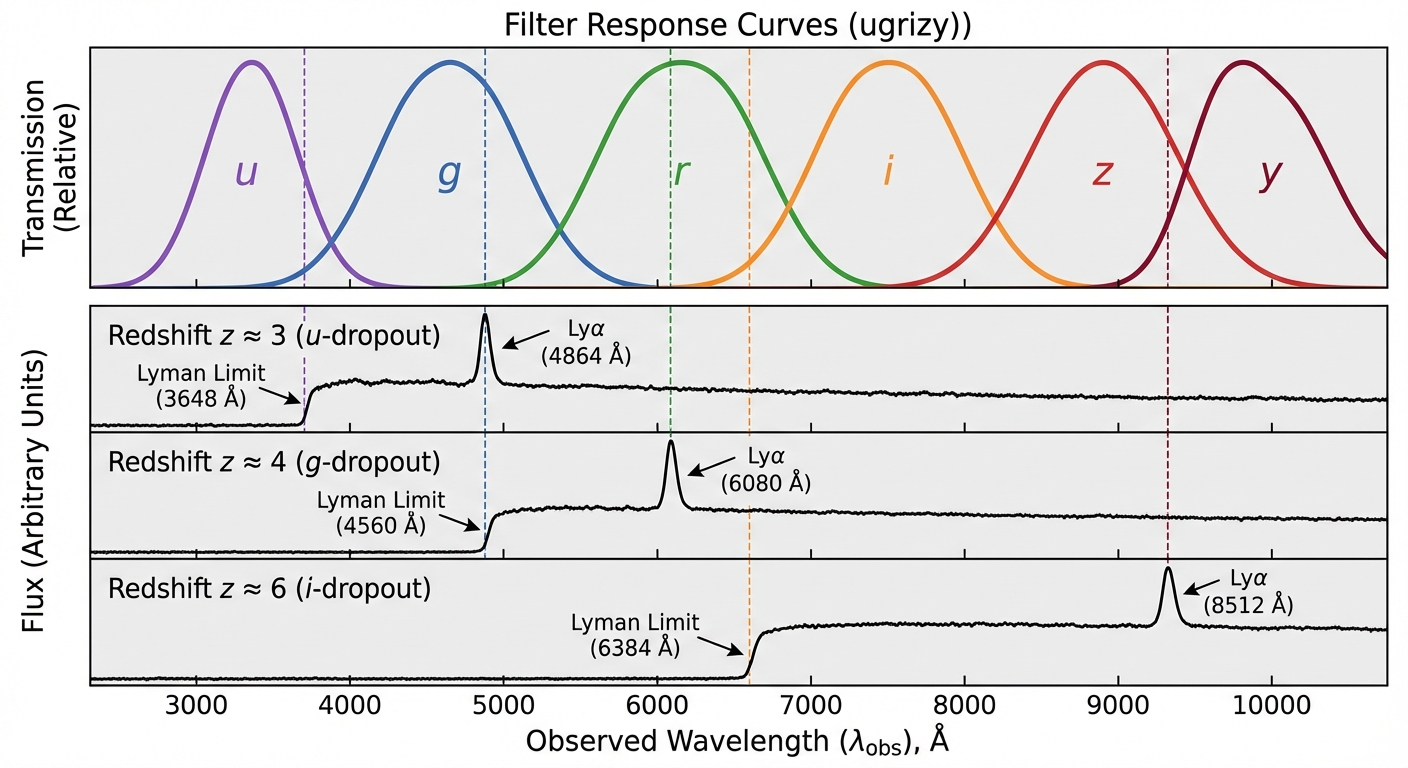
(Actually this is not possible in reality, because the noise is too low.)
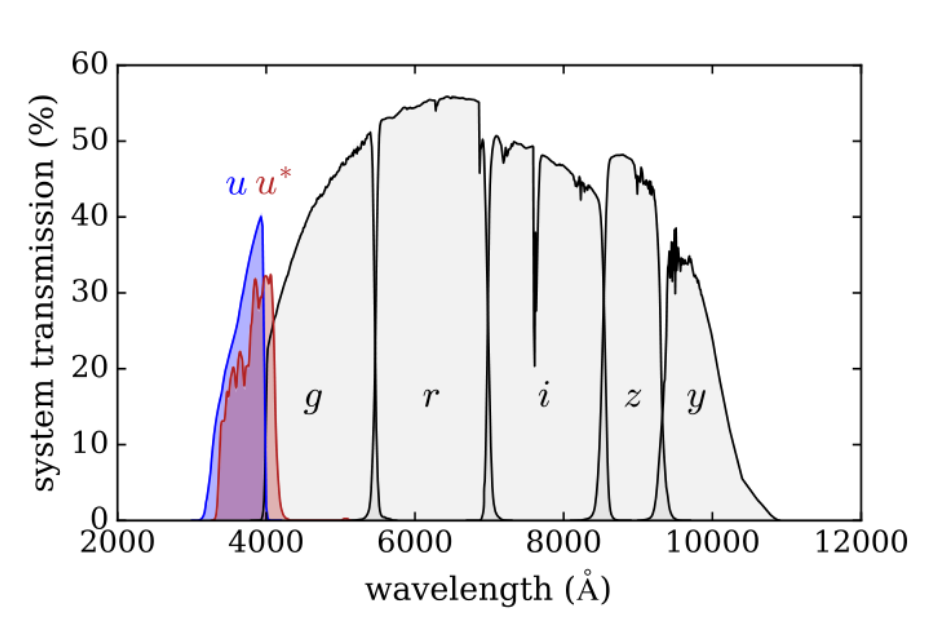
(This is the picture from the article.)
Review of Previous Research
- Core objective of estimating photometric redshifts of Lyman-break galaxies (LBG): probe the matter distribution of the universe in the relatively unexplored redshift range of $2 < z < 4.5$
- Primary goal of Ruhlmann-Kleider et al. (2024) is to develop an optimized target selection method for LBGs using deep imaging data to reach higher densities than current quasar samples.
Reproduction of the Color Cut
Apply the unrefined color-cut according to Ruhlmann-Kleider et al. (2024):
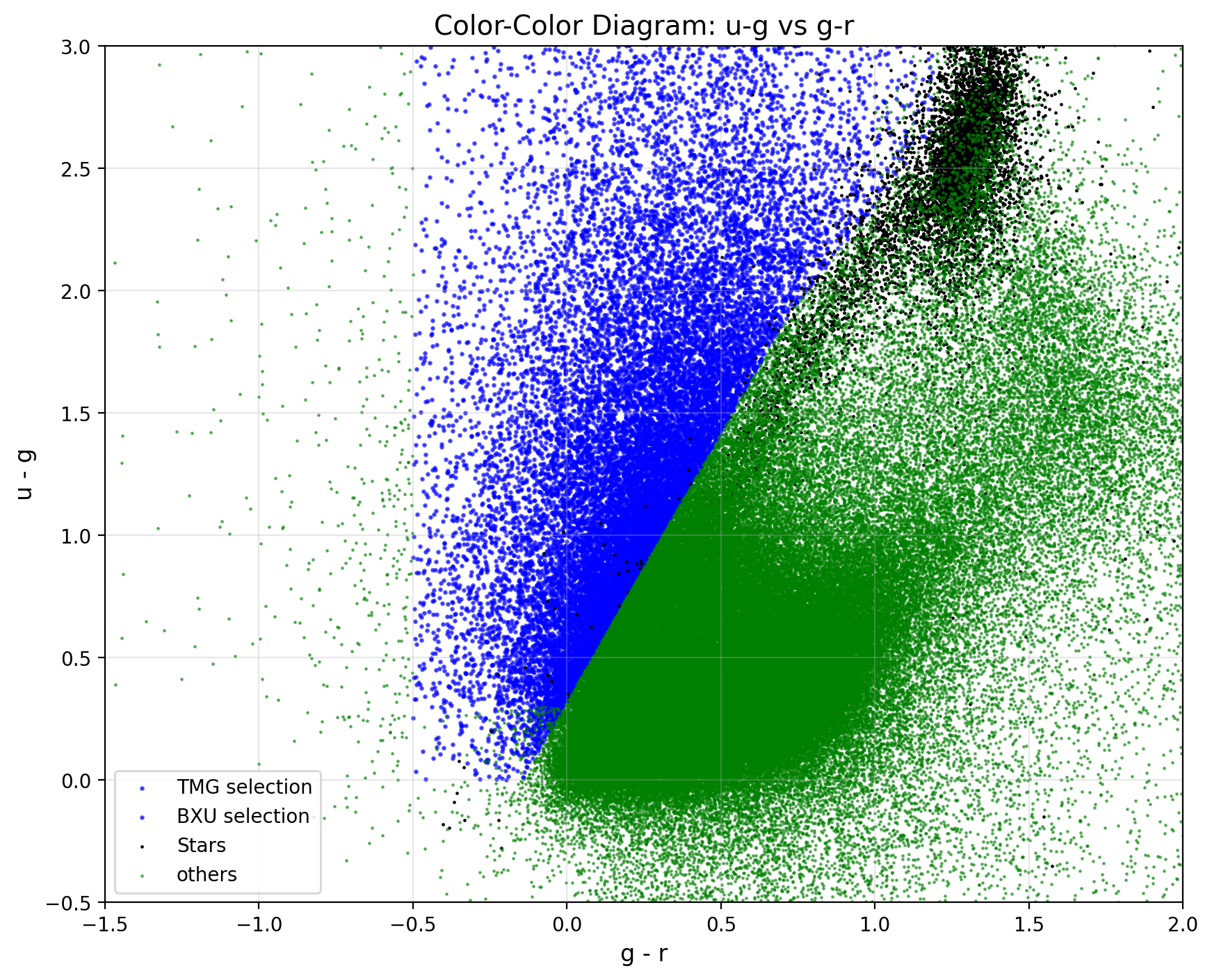
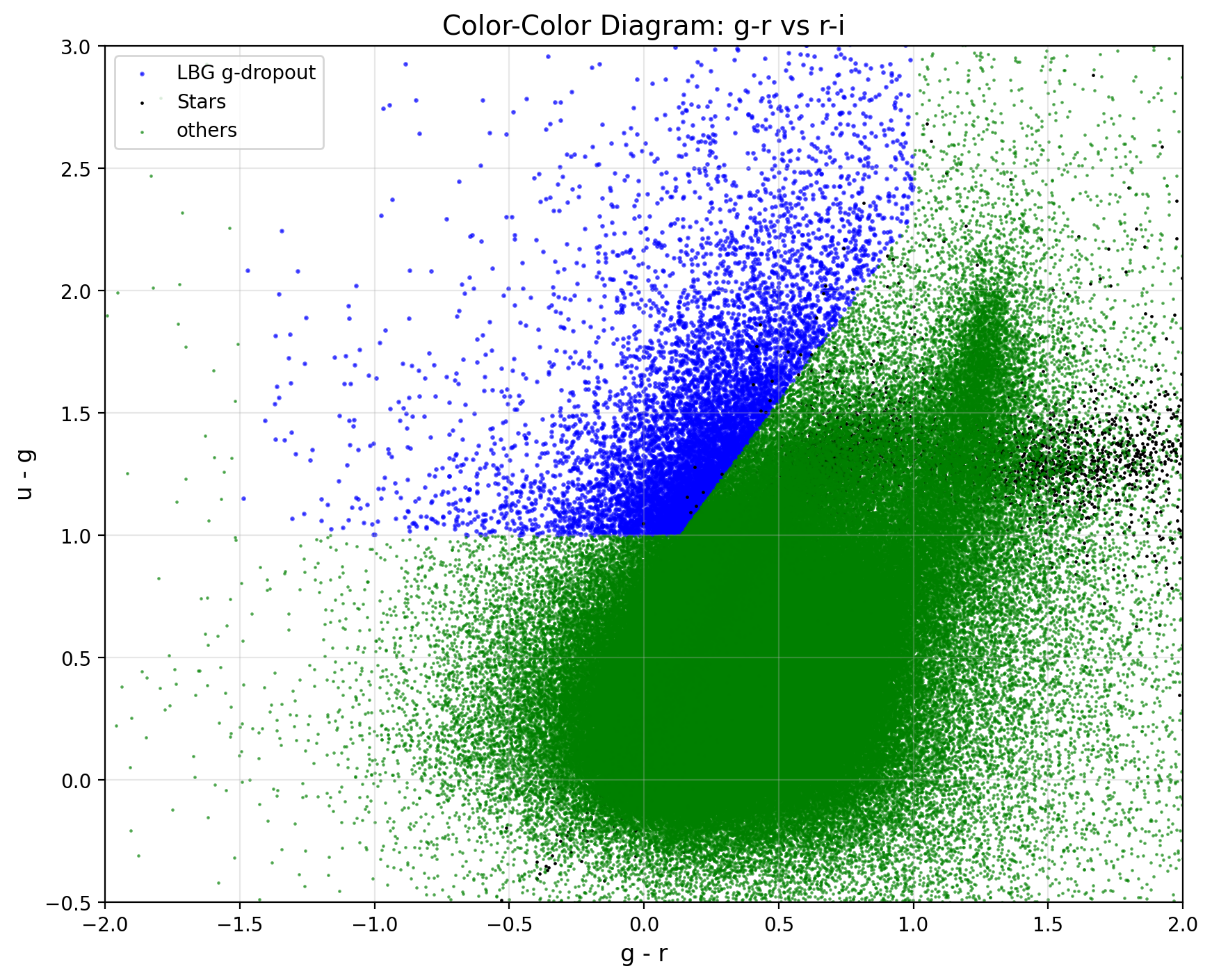
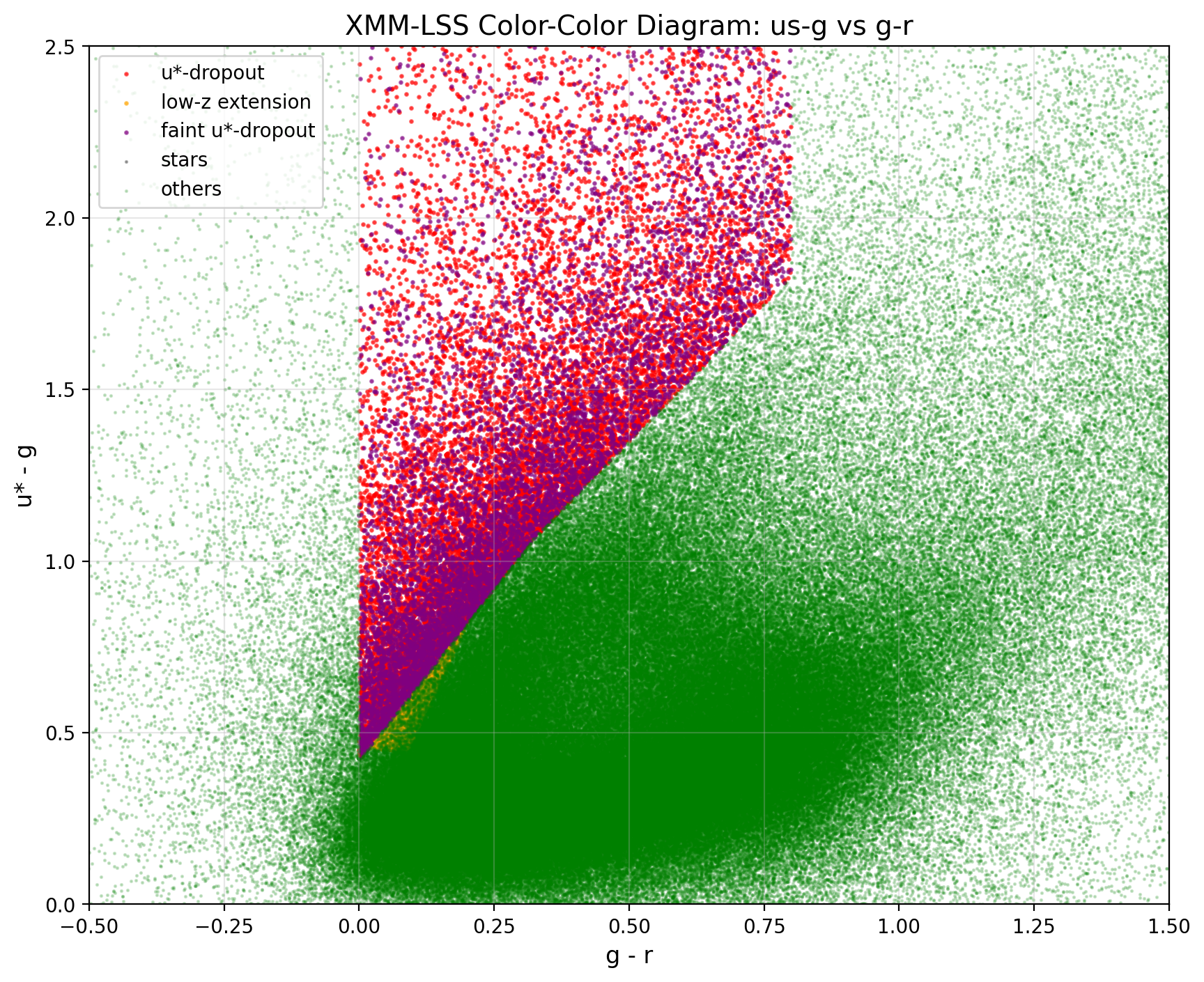
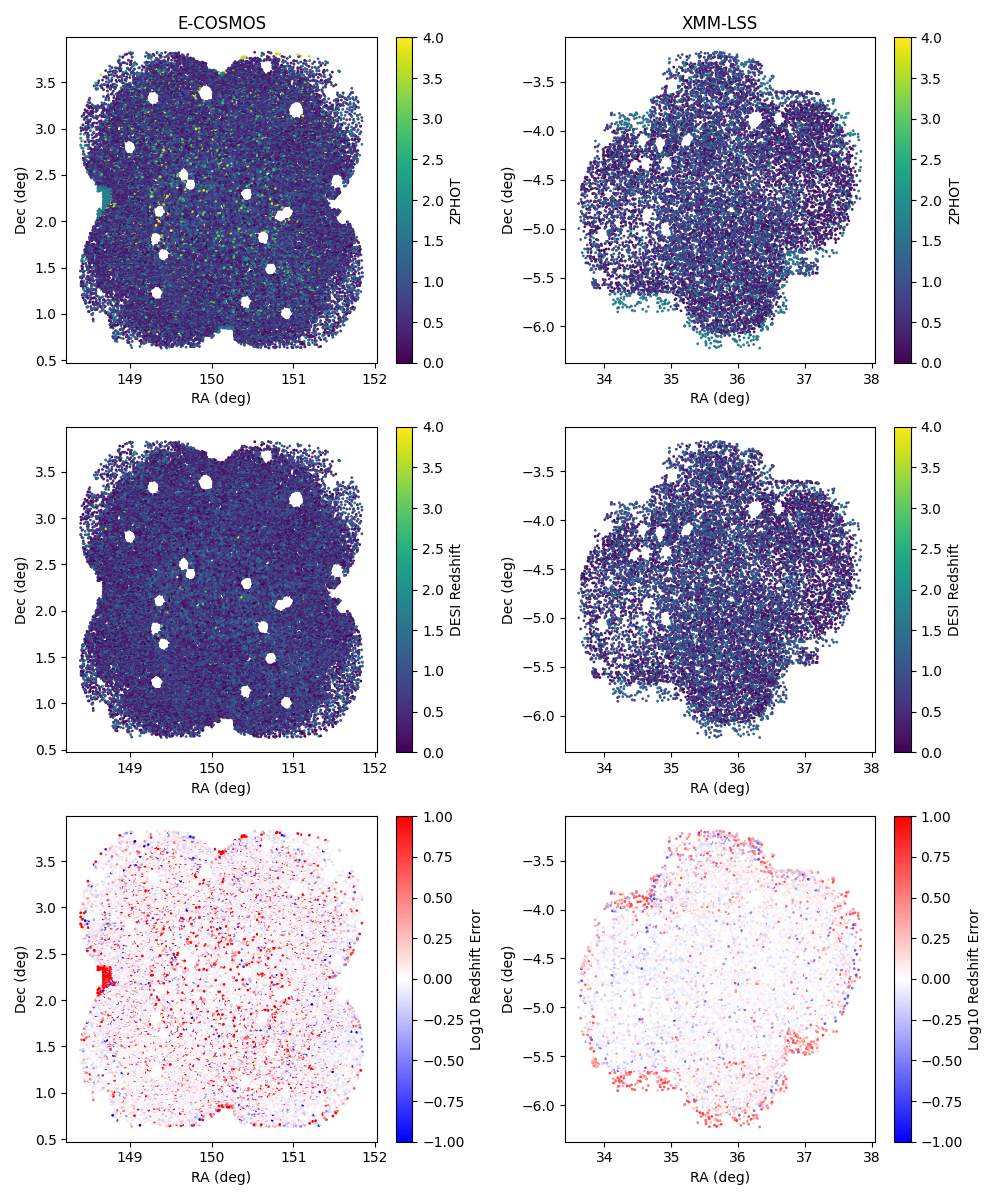
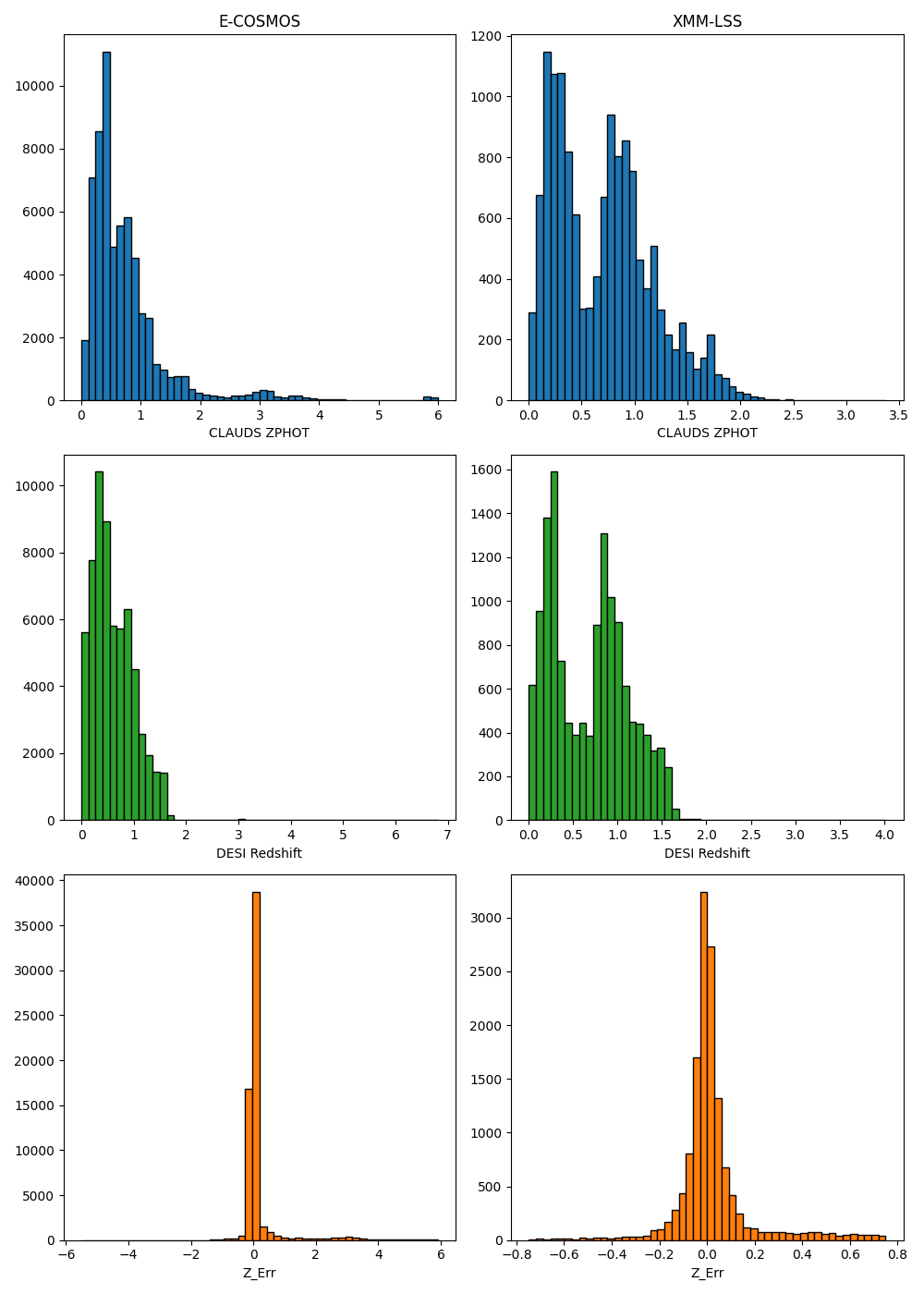
Crossmatching Data from CLAUDS & DESI
将 CLAUDS 的数据导入后,需要下载并匹配 DESI 的光谱红移数据.
首先我们根据 CLAUDS 数据天区 RA,DEC 的边界,扩大 $0.5^{\circ}$ 下载 DESI 的 DR1 库中的编号、坐标、光谱红移、光谱形态、红移质量和形态特征. 为了使数据更有效,我们只选取了高质量红移、光谱特征非恒星 (spectype!='STAR')、形态特征非点源(morphtype!='PSF') 的数据.
Crossmatching Data from CLAUDS & DESI
因为 DESI 对光谱特征为''高红移星系''的判断主要依据 $372.7\text{ nm}$的 OII 线,然而其光谱仪的极限为 $980\text{ nm}$,当 $z>1.63$ 时识别不了这个星系,可能会被分到''QSO''标签里. 所以我们只筛选 spectype!='STAR'而不是 spectype='GALAXY',并同时用 morphtype!='PSF' 筛去''真 QSO''.
(然后赵老师今天上午直接发了一份数据,以上的工作我似乎白做了?)
Crossmatching Data from CLAUDS & DESI
匹配:我们使用 astropy.coordinates.match_coordinates_sky,这可以初步将 CLAUDS 与 DESI 匹配,并输出角距离. 因为 CLAUDS 数据的平均距离为约为 $0.4''$,我们只选取角距离小于 $0.4''$ 的数据以筛去明显不是同一天体的数据.
Crossmatching Data from CLAUDS & DESI
match_coordinates_sky 不是简单的一个一个匹配两个源的数据 (算法耗时 $O(N\times M)$),而是对 DESI 建立了一个 $k$-$d$ 树:先将二维角坐标转化为单位球面上的三维坐标,然后像切蛋糕一样,把 3D 空间不断地一分为二,直到每个小格子里只剩下一个或几个星星. 然后 CLAUDS 的数据从树根开始往下走,进行''剪枝'',不需要遍历所有 DESI 的点,只需要遍历极少的一部分路径就能找到最近的那个点. 最终算法耗时从 $O(N\times M)$ 降至 $O(N\log M)$.
Crossmatching Data from CLAUDS & DESI
更进一步地,我们将 CLAUDS 的测光红移与 DESI 的光谱红移比对. 因为测光红移的偏差较大,我们暂时以 $\Delta z \leqslant 3.0$ 筛选. 我们还在考虑将 $r$ 波段的星等放入筛选条件,但因为一开始没有查到星等零点,暂时没有放入,会在后续研究中添加.
最后,将匹配到的光谱红移作为真值,与 CLAUDS 中匹配到的数据导出.
Crossmatching Data from CLAUDS & DESI